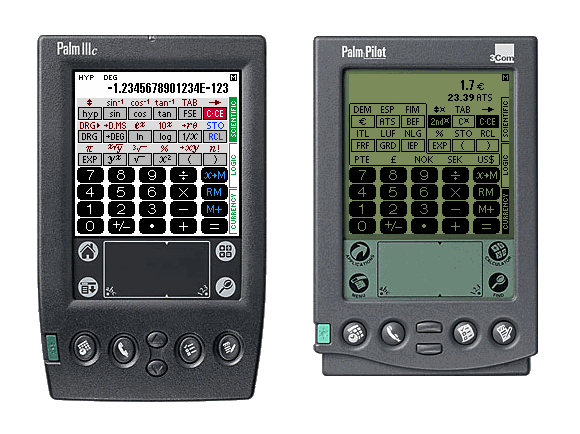
| SCIENTIFIC CALCULATOR FOR THE PALM HANDHELD COMPUTER | |
| MODEL SC-103PC |
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
 |
With the program SC-103PC you get a powerful and freely available scientific calculator for the Palm platform. Apart from scientific functions it also offers a full set of logical operations and conversions between different numeric systems. Additionally the calculator offers a currency mode for easy conversions between 17 different currencies as far as calculations with mixed currency units. The program is designed in a way, that it simulates the visual and operational aspects of a true calculator, such that the user will be immediately familiar with its interface.
1. BACKGROUND |
The calculator program SC-103PC can be executed on all devices equipped with the Palm Operating System version 2.0 or higher. In addition, it requires the freely available MathLib which is shipped as part of the calculator for your convenience.
The calculator program automatically adapts to single and multi color devices. Starting with version 1.26 of the SC-103PC, high resolution displays of SONY Clié devices and devices equipped with Palm Operating System version 5 or higher are also automatically detected and supported. There is no need for different versions of the program.
The calculator SC-103PC is shipped in three different languages: English, german and esperanto. Only menu items and dialog boxes have been translated; key and display labeling is identical in all versions. To select the desired language, you have to install the proper program module. Since the name of the program module is the same for all languages, you can only have one language version installed at the same time.
![]() The calculator program SC-103PC as well as the MathLib have to be installed
on your Palm device. The SC-103PC uses the MathLib for some of its
calculations.
If you don't know, how to install additional applications on your Palm
device, please refer to the instruction manual which is shipped
with your Palm device.
The calculator program SC-103PC as well as the MathLib have to be installed
on your Palm device. The SC-103PC uses the MathLib for some of its
calculations.
If you don't know, how to install additional applications on your Palm
device, please refer to the instruction manual which is shipped
with your Palm device.
Installation Procedure:
To display the preferences window, select the menu item "Preferences...", which is located in the "Options" menu.
 | 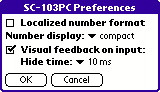 | 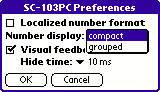 |
You can specify how the calculator should display the numbers. If you select "Localized number format", then seperator characters for numbers are used according to the global system preferences. Otherwise, commas are always displayed as dots and spaces are used to separate groups of three digits. Separator characters for groups of three digits will, however, only be used if you select "grouped" number display mode. In "compact" mode digits are displayed with equal spacing. Number settings only have effect in SCIENTIFIC and CURRENCY mode, the appearance of numbers in LOGIC mode can not be changed.
NOTE: All examples shown in these operating instructions assume that the "Localized number format" is not active and that the compact number display is selected. If you use other settings, then numbers displayed on your device may appear in a different format.
 . You can enable and
disable the flickering and additionally you can specify the amount of time
the display will be hidden to cause the flickering effect.
. You can enable and
disable the flickering and additionally you can specify the amount of time
the display will be hidden to cause the flickering effect.
The flickering of the display serves as a visual feedback to show you that the calculator has accepted your input. In addition, the pressed key will be highlighted but this effect is often not noticable during fast input because of the delay time of the usually used liquid crystal displays.
The flickering effect of the display can be made stronger or softer.
If a greater hide time is selected, the display will be hidden for a longer
time and the flickering effect will be stronger.
Select a value according to your personal taste.
Note: If the flickering effect is enabled, then the display will be dark as
long as you press a key. If you release the key before the selected
hide time is reached, then the display will stay dark at least until the
selected hide time is over.
Not all keys, e.g. number keys, result in a flickering effect of
the display because some result in a visual display change anyway
and also to simply prevent a too nervous display.
1. OPERATING MODES |
The calculator SC-103PC offers three general operating modes for different tasks. To select the desired operating mode there are the three vertically arranged fields at the right border of the display which are labeled SCIENTIFIC, LOGIC and CURRENCY. To select the desired operating mode, tip on the corresponding field with the stylus. The field indicating the currently selected mode is shown in a dark background color.
| On color devices | On B/W devices | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCIENTIFIC mode | 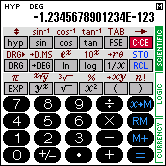 | 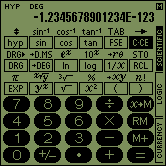 | ||
| LOGIC mode | 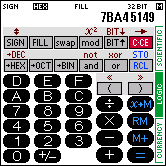 | 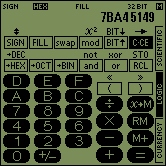 | ||
| CURRENCY mode | 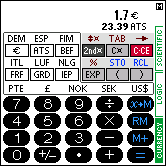 |  |
In SCIENTIFIC mode, the SC-103PC acts like a scientific calculator with 14 digits. In LOGIC mode, conversions between four different numeric systems are possible and basic arithmetic calculations and boolean operations can be performed. In CURRENCY mode, conversions between 17 different currencies and mixed currency calculations can be performed.
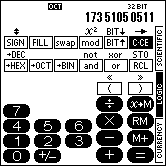
2. SCIENTIFIC MODE |
The Palm handheld can be used like a calculator with 14 digits. For that purpose the program SC-103PC has to be switched into SCIENTIFIC mode. You can activate the SCIENTIFIC mode by tapping on the corresponding field at the right border.
This is how the calculator in SCIENTIFIC mode looks like:
| On color devices | On B/W devices | |
|---|---|---|
 |  |
Now we will perform some simple calculations. Press the following keys and look at the display:
| Input | Display | ||||
| 123 | 123. | ||||
 | 123. | ||||
| 654 | 654. | ||||
 | 777. |
Did you get the right result? If not, press the
 key and try the same calculation again.
key and try the same calculation again.
Next, the value of pi ( ) should be recalled.
The symbol "
) should be recalled.
The symbol " " is located above the key
" is located above the key
 . Press the symbol.
. Press the symbol.
| Input | Display | ||||
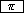 | 3.1415926535898 |
The Display now shows the value of  .
.
Now 104 should be calculated. For this operation the
function 10x will be used.
| Input | Display | ||||
4  | 10000. |
Following the most important keys will be outlined:
*  (Clear) (red rsp. dark key) (Clear) (red rsp. dark key) |
If this key is pressed immediately after input of numerical data or
after a recall of the memory contents, this data will be cleared.
In any other case, pressing the  key clears
the operator and/or the numerical data which have been entered.
The content of the memory will not be cleared by pressing the
key clears
the operator and/or the numerical data which have been entered.
The content of the memory will not be cleared by pressing the  key.
key.
| Input | Display | |||||
123  456 456 |
456. | |||||
 | 0. | |||||
786  | 912. | (123 + 789 = 912) | ||||
6  2 2  | 12. | |||||
 | 0. | |||||
6  2 2  | 12. | |||||
5  | 8. |
The  key can also be used to clear an error condition.
key can also be used to clear an error condition.
| Input | Display | ||
5  0 0  |  | ||
 |  |
*  (Display mode switch) (Display mode switch) |
With this key you can switch the display mode for the result of a calculation from floating point system (normal mode) to fixed point system (FIX), scientific notation (SCI), engineering notation (ENG) or vice versa.
| Input | Dispay | ||||
23  1000 1000  |  | ||||
 | 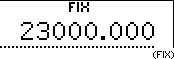 | ||||
 | 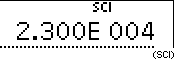 | ||||
 |  | ||||
*  (specifies the number of decimal digits) (specifies the number of decimal digits) |
In comibation with a number key, this key can be used to specify the number of
decimal digits (digits after the decimal point). Press the clear key
 so that "0." is displayed. Press the key
so that "0." is displayed. Press the key
 , then "0.000" (FIX mode) appeares on the display.
, then "0.000" (FIX mode) appeares on the display.
1. Specification of 2 decimal digits.
| Input | Display | ||
 2 2 | 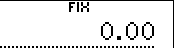 | ||
5  8 8  | 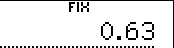 |
2. Specification of 5 decimal digits.
| Input | Display | ||
 5 5 | 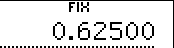 |
*  (specifies the angular mode) (specifies the angular mode) |
This key is used to specify the angular mode for numerical data for trigonometric functions, inverse trigonometrc functions and coordinate transformations.
| Input | Display | |||
 | (Degree) | |||
 |  | (Radian) | ||
 |  | (Grad) | ||
 |  | (Degree) |
180° = | DEG: Degree [°] RAD: Radian [rad] GRAD: Grad [g] |
*  (transforms between angular modes) (transforms between angular modes) |
This key is used for transformations between angular modes and simultaneously specifies the angular mode for numerical data for trigonometric functions, inverse trigonometrc functions and coordinate transformations.
| Input | Dispay | |||
| 180 |  | (Degree) | ||
 | 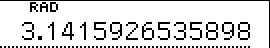 | (Radian) | ||
 |  | (Grad) | ||
 |  | (Degree) |
*  to to  , ,  , ,  and and  |
 :
Used to enter numbers in exponential notation (an "E" following the entered number appears on the display).
:
Used to enter numbers in exponential notation (an "E" following the entered number appears on the display).
| Input | Display | |||||
 4 4  3 3 | 4.E 003 | (4 × 103) | ||||
 | 4000. | |||||
 | -4000. |
 :
Used to enter negative numbers (or to inverse the sign from
negative to positive).
:
Used to enter negative numbers (or to inverse the sign from
negative to positive).
| Input | Display | |||||
1.23  | -1.23 | |||||
 5 5  | -1.23E-005 | (-1.23 × 10-5) | ||||
 | -0.0000123 | |||||
 | 0.0000123 |
*  (Backspace) (Backspace) |
With this key the last entered digit can be deleted.
| Input | Display | |||||
| 125 | 125. | |||||
 | 12. | |||||
| 3 | 123. | |||||
 478 478 | 478. | |||||
 | 47. | |||||
 | 4. | |||||
| 56 | 456. | |||||
 | 579. | (123 + 456 = 579) | ||||
1.456  19 19 | 1.456E 019 | |||||
 | 1.456E 001. | |||||
| 2 | 1.456E 012. | |||||
 1000 1000  | 1456000000. | (1.456 × 1012 / 1000 = 1456000000) |
Input:
12  45.6 45.6  32.1 32.1  789 789  741 741  213 213  | Result: 286.5 |
| a. | Input: 841  586 586  12 12  |
| Result: 41068.833333333 | |
| b. | Input: 427  54 54  32 32  7 7  39 39  2 2  |
| Result: 595.85714285714 |
Note that multiplication and division have priority over addition and subtraction. Internally, the calculator first calculates the multiplication and division.
Multiplication with a constant:Input: 3  5 5  | Result: 15 | |
Input: 10  | Result: 30 |
Division with a constant:
The value entered after the division sign acts as a constant.
Input: 15  3 3  | Result: 5 | |
Input: 30  | Result: 10 |
Note:
Depending on the priority, the calculator puts some calculations in pending state.
In case of chain calculations, the last calculation instruction,
taking into account the priority rules,
and the relevant numeric value are retained and can be used for further calculations
or as constants, respectively.
| a + b × c = | + bc | (Constant addition) | ||
| a × b ÷ c = | ÷ c | (Constant division) | ||
| a ÷ b × c = | a/b × | (Constant multiplication) | ||
| a × b - c = | - c | (Constant subtraktion) |
The independently accessible memory can be maintained with the three keys  ,
,
 and
and  . Before starting a calculation
clear the memory by pressing
. Before starting a calculation
clear the memory by pressing  and
and  .
.
If a value other than zero is stored in memory
" " is displayed.
" is displayed.
Input: 12  5 5  | |
| Result: 17 | |
For subtraction enter: 2  5 5    | |
| Result of this equation: -7 | |
Enter  to recall memory contents: 10 will be displayed. to recall memory contents: 10 will be displayed. | |
Input: 12  2 2   | |
| Result: 24 (replaces 10 in memory) | |
Input: 6  2 2  | |
Result: 4 : 28 : 28 | |
To subtract a value from memory contents, the keys  and
and  can be pressed.
can be pressed.
In addition to the memory which can be modified with the  key,
there are 10 memory slots available which can be modified with
key,
there are 10 memory slots available which can be modified with

 to
to 
 .
.
To read the contents of these memories you have to press the keys 
 to
to 
 just
like
just
like  for the independently accessible memory.
for the independently accessible memory.
To calculate trigonometric and inverse trigonometric equations and for
coordinate transformations the angular mode has to be assigned.
The assignment of the angular mode DEG, RAD or GRAD happens by pressing the
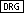 key.
key.
| Exercise: sin 30° + cos 40° | ||
| Angular mode to DEG | ||
Input: 30  + 40 + 40 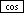  |
Result: 1.266044443119 | |
Exercise: cos 0,25 | ||
| Angular mode to RAD | ||
Input: 0.25 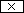   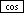 |
Result: 0.7071067811865 | |
| Exercise: sin-1 0,5 | ||
| Angular mode to DEG | ||
Input: 0.5  | Result: 30 | |
| Exercise: cos-1 -1 | ||
| Angular mode to RAD | ||
Input: 1 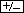  |
To input a negative number, press the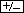 key after entering the number. key after entering the number. | |
Result: 3.1415926535898 (Value of  ) ) | ||
The results of inverse trigonometric functions are only valid between the following ranges:
 = sin-1 x, = sin-1 x,  = tan-1 x = tan-1 x |
 = cos-1 x = cos-1 x | |
DEG: -90 <=  <= 90 [°] <= 90 [°] |
DEG: 0 <=  <= 180 [°] <= 180 [°] | |
RAD: - /2 <= /2 <=  <= <=  /2 [rad] /2 [rad] |
RAD: 0 <=  <= <=  [rad] [rad] | |
GRAD: -100 <=  <= 100 [g] <= 100 [g] |
GRAD: 0 <=  <= 200 [g] <= 200 [g] |
| Exercise: sinh 4 | ||
Input: 4   |
Result: 27.289917197128 | |
| Exercise: sinh-1 9 | ||
Input: 9   |
Result: 2.8934439858859 |
| Exercise: 202 | ||
Input: 20 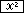 | Result: 400 | |
| Exercise: 33 and 34 | ||
Input: 3 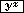 3 3  |
Result: 27 | |
Input: 3 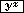 4 4  |
Result: 81 |
| Exercise: Square root of 25 | ||
Input: 25 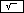 | Result: 5 | |
| Exercise: Cube root of 27 | ||
Input: 27 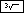 | Result: 3 | |
| Exercise: Fourth root of 81 | ||
Input: 81 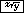 4 4  |
Result: 3 |
| Exercise: ln 21, log 173 | ||
| Natural Logarithms | ||
Input: 21 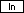 | Result: 3.0445224377234 | |
| Common Logarithms | ||
Input: 173 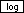 | Result: 2.2380461031288 |
| Exercise: e3,0445 | ||
Input: 3.0445 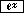 | Result: 20.999528813094 (see ln 21) | |
| Exercise: 102,238 | ||
Input: 2.238  | Result: 172.98163592151 (see log 173) |
| Exercise: 1/6 + 1/7 | ||
Input: 6 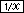  7 7 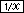  |
Result: 0.3095238095238 |
| Exercise: 170! | |
Input: 170  | |
| Result: 7.257415615308E 306 (= 7,257415615308 × 10306) | |
On calculating the factorial it is easily possible to overflow the calculation limits of the SC-103PC which results in the error indication "E". The section Calculation Range discusses the calculation limits of the calculator.
| Exercise: 8P3 = 8!/(8-3)! | |
Input: 8    8 8  3 3    | |
| Result: 336 | |
| Exercise: 45% of 2780 (2.780 × 45/100) | ||
Input: 2780  45 45   |
Result: 1251 | |
| Exercise: 200 - 200 × 30/100 | ||
Input: 200  30 30   |
Result: 140 |
To convert an angle or time (°, ', ", rsp. hours, minutes, seconds) to its decimal equivalent the degrees have to be given as integer portion and the minutes and seconds as decimal digits.
Exercise: Transformation of 12°47'52" to its decimal equivalent
Input: 12.4752  |
Result: 12.797777777778 |
When converting decimal degrees to the equivalent
degrees/minutes/seconds, the answer is broken down:
integer portion = degrees; 1st and 2nd decimal digits = minutes;
3rd and 4th digits = seconds; and 5th through end decimal digits
are decimal seconds.
Exercise: Conversion of the decimal angle 24.7256 to its degree/minute/second equivalent
Input: 24.7256  | Result: 24.433216 or 24°43'32" |
A horse has leap times of 2 minutes 25 seconds, 2 minutes 38 seconds and 2 minutes 22 seconds. What is the average running time?
Input:
0.0225   0.0238 0.0238 
 0.0222 0.0222   | |
| Result 1: 0.1236111111111 | |
Input:  3 3  | |
| Result 2: 0.0412037037037 | |
Input:  | |
| Result 3: 0.0228333333333 or the average time is 2 minutes 28 seconds. | |
Converting rectangular coordinates to polar (x, y  r,
r,  ).
).
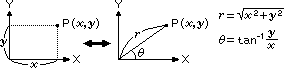 |
DEG: RAD: GRAD: |
0 <= |  | <= 180 | <= 1800 <= |  | <= | <=  0 <= |  | <= 200 | <= 200 |
Convert rectangular coordinates x = 6 and
y = 4 to polar coordinates.
Angular mode: DEG
Input: 6  4 4  |
Result: 7.211102550928 (r) | |
Input:  |
Result: 33.69006752598 ( ) ) |
Calculate the magnitude and direction (phase) in a vector i = 12 + j9
Input: 12  9 9  |
Result: 15 (r) | |
Input:  |
Result: 36.869897645844 ( ) ) |
Converting polar coordinates to rectangular
(r, 
 x, y).
x, y).
Solve for P(14,  /3), r = 14,
/3), r = 14,
 0
0  /3
/3
Angular mode: RAD
Input:   3 3
  14 14 
 | |||||||||
| Result: 7 (x) | |||||||||
Input:  | |||||||||
| Result: 12.124355652982 (y) | |||||||||
 =
=  /3
is entered first and is replaced by r = 14 by
pushing the
/3
is entered first and is replaced by r = 14 by
pushing the  key after entering r.
key after entering r.
Usage of the parenthesis keys 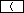 and
and
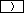 is required if series of calculations
are combined together and the priority of operations has to be changed.
is required if series of calculations
are combined together and the priority of operations has to be changed.
After pressing the 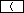 key, "( )" is displayed in the
top of the display.
key, "( )" is displayed in the
top of the display.
Calculations between parenthesis have priority over all other calculations.
The parentheses can be nested more than once. First the calculations
between the innermost parenthesis will be made.
| Exercise: 12 +42 ÷ (8 -6) | |
Input: 12  42 42  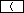 8 8  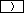  | |
| Result: 33 | |
| Exercise: 126 ÷ {(3 + 4) × (3 - 1)} | |
Input: 126  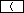 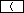 3 3  4 4    3 3  1 1    | |
| Result: 9 | |
Hint:
It is not neccessary to close the parenthesis immediately before
the  key (or
key (or  key).
key).
The number of decimal digits in a calculation result can be specified; to do this
use the  key in combination with the keys
key in combination with the keys  to
to  . In this case, the display has to be switched to
fixed point (FIX), scientific notation (SCI) or engineering notation (ENG).
. In this case, the display has to be switched to
fixed point (FIX), scientific notation (SCI) or engineering notation (ENG).
  |
 | No decimal digits. (The number will be roundet to the next integer number.) | |
  |
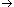 | One decimal digit. (The number will be roundet to the first decimal digit.) | |
  |
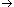 | Nine decimal digits. (The number will be roundet to the 9th decimal digit.) |
To clear the TAB setting (definition of places after decimal digit) leave the calculator application and restart it again. Then the normal display will be shown again.
Example:
 9 9 | |||
0.5  9 9  |
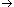 | 0.055555556 (FIX mode) (The number is roundet to the 9th place after decimal digit.) | |
 |
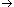 | 5.555555556E-002 (SCI mode) (The mantissa is roundet to the 9th place after decimal digit.) | |
  |
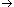 | 5.556E-002 (SCI mode) (The mantissa is roundet to the third place after decimal digit.) | |
 |
 | 55.556E-003 (ENG mode) | |
 |
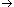 | 0.0555555555556 |
The program is provided with a function that judges the priority level of individual calculations; thus, you can enter your calculations in the same order as in a given mathematical formula. The following table shows the priority level of individual calculations.
Example:
Key operation and sequence of calculation in
5 + 2 × sin 30 + 24 × 53 =
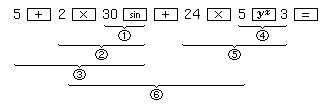
The numbers  -
-  show the sequence of the
calculations.
show the sequence of the
calculations.
When calculations with higher priority are executed, those with lower priority must be saved in the meantime.
The program is equipped with additional memories for such pending operations.
As these memories are also used for calculations with parentheses,
calculations can be performed according to a given mathematical formula
unless parentheses and pending operations exceed 30 levels in total.
 DEG,
DEG, 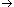 D.MS, etc.) are
calculated immediately after key operation without being retained.
D.MS, etc.) are
calculated immediately after key operation without being retained.
Example:
 | Pending of 1 level |
 | Pending of 2 levels |
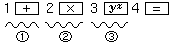 | Pending of 3 levels |
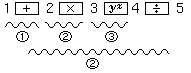 | By pressing the
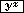 key, 3 pending levels are reached. After pressing the key, 3 pending levels are reached. After pressing the
 key the calculations "yx"
will be performed with highest priority and "×" with the same priority.
Thus, after pressing the key the calculations "yx"
will be performed with highest priority and "×" with the same priority.
Thus, after pressing the  key, two pending levels remain. key, two pending levels remain. |
Example:
| i) |  | 4 numbers and operations stay pending. |
| ii) | 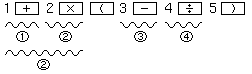 | After pressing
the  key first the calculation between parentheses
3 - 4 ÷ 5 will be performed;
2 calculations stay pending. key first the calculation between parentheses
3 - 4 ÷ 5 will be performed;
2 calculations stay pending. |
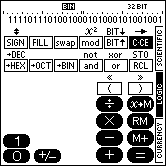
3. LOGIC MODE |
Computer engineers and programmers are in need of simple conversions between various numeric systems as well as for calculations with boolean logic. With the calculator SC-103PC this problem is solved by providing the LOGIC mode. The LOGIC mode can be selected by tapping on the corresponding field at the right border.
Note:
You should first read the sections "Calculations"
and "Basic Usage" in the chapter
"3. SCIENTIFIC MODE", to get familiar
with the operation of the calculator and its basic functions before you
use the LOGIC mode.
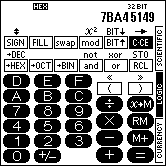
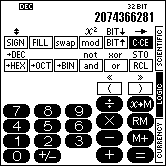
This is how the calculator looks in LOGIC mode (hexadecimal notation selected):
| On color devices | On B/W devices | |
|---|---|---|
 |  |
The calculator can operate with integer values up to a bit width of 32 bits in four different numeric systems.
 |
To convert a number to its hexadecimal equivalent; at the same time
the calculator will be switched to hexadecimal notation HEX.
( is shown in the displayed.) is shown in the displayed.) |
 |
To convert a number to its decimal equivalent; at the same time
the calculator will be switched to decimal notation DEC.
( is shown in the display.) is shown in the display.) |
 |
To convert a number to its octal equivalent; at the same time
the calculator will be switched to octal notation OCT.
( is shown in the display.) is shown in the display.) |
 |
To convert a nubmer to its binary equivalent; at the same time
the calculator will be switched to binary notation BIN.
( is shown in the display.) is shown in the display.) |
Exercise:
Conversion from decimal 30 to hexadecimal notation:
Press  key if calculator is not currently
in decimal notation (
key if calculator is not currently
in decimal notation ( is displayed).
is displayed).
| Input | Display | ||||
30  | 1E |
Exercise:
Further conversion of hexadecimal 1E to binary format:
| Input | Display | ||||
 | 11110 |
 |
The hexadecimal notation system is mainly used in computer programming. The base for a hexadecimal number is 16; hexadecimal numbers consist of the digits 0 to 9 and the major letters A to F, which stand for the numbers 10 to 15 in the decimal system.
Keys for the letters A to F will be shown as soon as the calculator is
in hexadecimal notation.
The symbol |
 |
In LOGIC mode even in decimal notation only integer values with a bit width of a maximum of 32 bits can be handled.
In decimal notation only the keys for the digits 0 to 9 are shown.
The symbol |
 |
The base for a octal number is 8; octal numbers consist of the digits 0 to 7.
In octal notation only the keys for the digits 0 to 7 are shown.
The symbol |
 |
The binary notation system is mainly used in computer programming. The base for a binary number is 2; binary numbers consist of the digits 0 and 1.
In binary notation only the keys for the digits 0 and 1 are shown.
A smaller font is used so all of the 32 positions can be displayed in
one row. Additionally, a ruler is shown above the digits to support the
identification of nibbles, bytes and words.
The symbol |
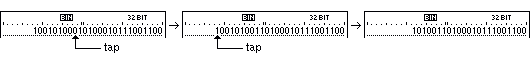
In the binary notation system a digit can be swapped from 0 to 1
and vice versa by tapping on the digit position below the ruler.
If an empty area is tapped then the digit 1 will be set there.
With this functionality it is possible to directly modify the bits
of a value.
The calculator can be switched to bit widths of 8, 16 and 32 bits
which are commonly used in the computer industry. With the
 key the next higher and with the
key the next higher and with the
 key the next lower bit width is selected.
The currently selected bit width is shown in the display.
key the next lower bit width is selected.
The currently selected bit width is shown in the display.
With the  key you can switch leading zeros on
and off.
Press the
key you can switch leading zeros on
and off.
Press the  key once to show numbers with leading
zeros filled to the selcted bit width (
key once to show numbers with leading
zeros filled to the selcted bit width ( will be shown in the display).
Press the
will be shown in the display).
Press the  key once more to switch back to normal number display.
If
key once more to switch back to normal number display.
If  is activated then leading zeros can be entered during input.
is activated then leading zeros can be entered during input.
Example:
Settings:  ,
,  notation,
notation, 
| Input | Display | ||||||
1AB  | 1AB |   | |||||
 | 01AB |    | |||||
 | 0000 01AB |  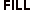  | |||||
| Input | Display | ||||||
| 000AB8 | 00 0AB8 |  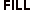  | |||||
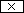 | 0000 0AB8 |    | |||||
456  | 002E 79D0 |    | |||||
 | 2E 79D0 |   |
With the  key, the calculator can be switched
between signed and unsigned mode. In the display the symbol
key, the calculator can be switched
between signed and unsigned mode. In the display the symbol
 appears if the signed mode is active.
appears if the signed mode is active.
Signs are only shown in HEX, DEC and OCT notations. In the BIN notation only the bits are shown, always without a sign.
With the  key the sign of a number can be changed.
If the sign of a positive number is changed, the 2's complement
of the number is calculated. In signed mode the number will then be
shown as negative number in unsigned mode as 2's complement.
key the sign of a number can be changed.
If the sign of a positive number is changed, the 2's complement
of the number is calculated. In signed mode the number will then be
shown as negative number in unsigned mode as 2's complement.
Example:
Settings:  ,
,  notation,
notation, 
| Input | Display | ||||||
180  | -180 |    | |||||
 | FE80 |    | |||||
 | 1111111010000000 |    |
The selected bit width in combination with the sign mode has influence on the number range which can be handled. In contrast to the SCIENTIFIC mode, too big or too small numbers do not lead to an error condition in LOGIC mode but to an overflow.
| Bit Width | Num. Sys. | Sign Mode | Number Range | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 BIT | HEX | 0 | ~ | FF | |
| 8 BIT | HEX | SIGN | -80 | ~ | 7F |
| 8 BIT | DEC | 0 | ~ | 255 | |
| 8 BIT | DEC | SIGN | -128 | ~ | 127 |
| 8 BIT | OCT | 0 | ~ | 377 | |
| 8 BIT | OCT | SIGN | -200 | ~ | 177 |
| 8 BIT | BIN | 0 | ~ | 11111111 | |
| 8 BIT | BIN | SIGN | 0 | ~ | 11111111 |
| 16 BIT | HEX | 0 | ~ | FFFF | |
| 16 BIT | HEX | SIGN | -8000 | ~ | 7FFF |
| 16 BIT | DEC | 0 | ~ | 65535 | |
| 16 BIT | DEC | SIGN | -32768 | ~ | 32767 |
| 16 BIT | OCT | 0 | ~ | 17 7777 | |
| 16 BIT | OCT | SIGN | -10 0000 | ~ | 7 7777 |
| 16 BIT | BIN | 0 | ~ | 1111111111111111 | |
| 16 BIT | BIN | SIGN | 0 | ~ | 1111111111111111 |
| 32 BIT | HEX | 0 | ~ | FFFF FFFF | |
| 32 BIT | HEX | SIGN | -8000 0000 | ~ | 7FFF FFFF |
| 32 BIT | DEC | 0 | ~ | 4294967295 | |
| 32 BIT | DEC | SIGN | -2147483648 | ~ | 2147483647 |
| 32 BIT | OCT | 0 | ~ | 377 7777 7777 | |
| 32 BIT | OCT | SIGN | -200 0000 0000 | ~ | 177 7777 7777 |
| 32 BIT | BIN | 0 | ~ | 11111111111111111111111111111111 | |
| 32 BIT | BIN | SIGN | 0 | ~ | 11111111111111111111111111111111 |
Exercise:
Solve of 250 + 15 with unsigned 8 bit arithmetic (overflow calculation):
Press the  key to select decimal notation
(
key to select decimal notation
( is shown in the display).
is shown in the display).
Press the  until
until  is shown in display.
is shown in display.
With the  key select unsigned mode
(symbol
key select unsigned mode
(symbol  cleared in display).
cleared in display).
| Input | Display | ||||||
250  15 15  |
9 |   |
Exercise:
Display the result of the last calculation in binary notation:
| Input | Display | ||||||
 | 1001 |   |
The arithmetic operations addition, subtraction, multiplication and division can be used like in SCIENTIFIC mode. But only integer values can be handled.
Exercise:
Addition of two hexadecimal numbers
A4 + BA =
| Input | Display | ||||||
  | 0 |   | |||||
A4  BA BA  |
15E |   |
Exercise:
4 × 4 =
| Input | Display | ||||||
  | 0 |   | |||||
4 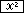 |
10 |   |
Exercise:
32 bit multiplication of the octal number 73 with the binary number 110
and display of the result as a decimal number
73 oct × 110 bin =
Press  until
until  is shown in display
is shown in display
| Input | Display | ||||||
  | 0 |   | |||||
73   | 111011 |   | |||||
110  | 101100010 |   | |||||
 | 354 |   |
Exercise:
(12 + D) × B =
| Input | Display | ||||||
  | 0 |   | |||||
 12 12
 D D   B B  |
155 |   |
Exercise:
| 43A | - | 3CB | = | |
| +) | A38 | - | 2FB | = |
| --------------- | ||||
| total | ||||
| Input | Display | ||||||
  | 0. |   | |||||
43A  3CB 3CB  |
6F |   | |||||
A38  2FB 2FB  |
73D |   | |||||
 | 7AC |   |
The following hints have to be noted:
Examples:
Input: E  3 3  |
Result: 4 |   | ||
Input: B  3 3  2 2  |
Result: 6 |   |
With the modulo operation the remainder of a division can be computed.
Input: E  3 3  |
Result: 2 |   |
By pressing the  key it is possible to
calculate the complement of a number in a simple way.
Settings: Unsigned mode (symbol
key it is possible to
calculate the complement of a number in a simple way.
Settings: Unsigned mode (symbol  is not shown,
is not shown,
 notation,
notation, 
Input: AB  |
Result: FFFF FF55 |   |
The operators of the boolean algebra AND, OR, XOR (exclusive or) and NOT can be used. In a logical operation two numbers will be transformed to binary representation (2's complement) and the logical relation will then be evaluated for every bit pair.
The following section will shown the results of the logical operators for these bit evaluations:
| AND | OR | XOR | NOT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
After every bit pair has been assigned the corresponding result (a 1 or a 0) according to the above table, the resulting binary number will be converted back to the selected numeric system. This number is the result of the logical operation.
Example: ,
,  notation,
notation,
 , please perform the following calculations:
, please perform the following calculations:
41 AND 27  gives 9 | 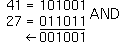 |
||||
Input: 41  27 27  |
Result: 9 |    | 41 OR 27 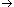 gives 59 | 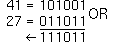 |
|
Input: 41  27 27  |
Result: 59 |    | 41 XOR 27 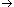 gives 50 | 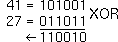 |
|
Input: 41  27 27  |
Result: 50 |    | NOT 3 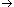 gives -4 (2's complement) | 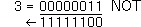 |
|
Input:3  |
Result: -4 |    | |||
NOT x can generaly be computed with the equation NOT x = -(x + 1).
 and
and  it is possible
to perform bit shift operations. Thereby the value will be transformed
to binary representation and the single bits will be shiftet to the left or the right
by the given amount. The result will be transformed back to
the selected numeric system which yields the result of the operation.
it is possible
to perform bit shift operations. Thereby the value will be transformed
to binary representation and the single bits will be shiftet to the left or the right
by the given amount. The result will be transformed back to
the selected numeric system which yields the result of the operation.
During the bit shift right operation the single bits of a value will be shiftet to the right by the given amount of positions. This is equivalent to a division by the power of 2.
Example:| decimal | binary | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| before shifting | 80 | 01010000 | |
| after shifting | 10 | 00001010 |
| Input: | Display: | ||||||
80  3 3 | 10 |  |
In signed mode ( ) an arithmetical shift right
will be performed whereas in unsigned mode a logical shift right is executed.
Arithmetical shift means that the sign of a number is retained; logical shift right always
results in a cleared sign bit, treating all bits equal.
) an arithmetical shift right
will be performed whereas in unsigned mode a logical shift right is executed.
Arithmetical shift means that the sign of a number is retained; logical shift right always
results in a cleared sign bit, treating all bits equal.
 ,
, 
| Input: | Result: | ||||||
  | 0 |    | |||||
120  | -120 |    | |||||
 | 10001000 |    | |||||
 1 1  | 11000100 |    | |||||
 | -60 |    |
| Input: | Result: | ||||||
 | 196 |   | |||||
 2 2  | 49 |   | |||||
 | 110001 |   |
During the bit shift left operation the single bits of a value will be shiftet the given amount of positions to the left. This is equivalent to a multiplication with the power of 2.
Example:| decimal | binary | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| before shifting | 3 | 0000 0011 | |
| after shifting | 12 | 0000 1100 |
| Input: | Display: | ||||||
3  2 2 | 12 |  |
 key the bytes of a 16 bit or 32 bit number
will be swapped. This allows conversions from"little-endian" to "big-endian" format and vice versa.
key the bytes of a 16 bit or 32 bit number
will be swapped. This allows conversions from"little-endian" to "big-endian" format and vice versa.
Example:
Settings: Unsigned mode (symbol  is not shown),
is not shown),
 notation,
notation,

| Input | Display | ||||||
| 1234ABCD | 1234 ABCD |   | |||||
 | CDAB 3412 |   | |||||
 | 3412 |   | |||||
 | 1234 |   |
In 8 bit notation the nibbles will be swapped:
Example:
Settings: Unsigned mode (symbol  is not shown),
is not shown),
 notation,
notation, 
| Input | Display | ||||||
| AB | AB |   | |||||
 | BA |   |
During the processing of complex expressions the calculator follows a set of predefined priorities which determine the sequence in which the operators have to be applied. In LOGIC mode, the same rules for priority of operators and parenthesis are valid as described in SCIENTIFIC mode in section "Priority Levels of Operations" but the additional boolean operators have to be taken into account:
1. Functions like not or x2
2. ×, ÷, mod
3. +, -
4. «, »
5. and
6. xor
7. or
8. =, M+
(Calculations which are on the same priority level are
executed in sequence.)
5. CURRENCY MODE |
The CURRENCY mode offers easy conversions between 17 different currency units and calculations with mixed currencies. The conversion factors (exchange rate) and currency symbols can be freely defined by the user. The calculator is shipped with the 12 Euro related national currencies and the Euro predefined. Each currency is assigned to a key. The CURRENCY mode can be selected by tapping on the corresponding field at the right border.
Note:
You should first read the sections "Calculations"
and "Basic Usage" in the chapter
"3. SCIENTIFIC MODE", to get familiar
with the operation of the calculator and its basic functions before you
use the CURRENCY mode.
This is how the calculator looks in CURRENCY mode (hexadecimal notation selected):
| On color devices | On B/W devices | |
|---|---|---|
 |  |
The CURRENCY mode has a display with two lines. User inputs are displayed in the first line. In the second line the entered or calculated value can instantly be viewed in a different currency. The numbers displayed in the two lines always represent the same value but in different currency units.
Following the most important keys will be outlined:
* Currency keys  , ,
 and so on and so on |
With the currency keys the currency unit of the number in the first display line can be selected.
The key area with the currency keys is surrounded by a thin line.
By pressing the  key for example the currency DEM will be assigned
to the value oft the first line in the display. During input of a number the currency unit can
be assigned at any time without effecting the numerical value.
key for example the currency DEM will be assigned
to the value oft the first line in the display. During input of a number the currency unit can
be assigned at any time without effecting the numerical value.
*  (specify second line) (specify second line) |
With the  key you specify the second
display line. The consecutively pressed key will the be related to the second
display line instead of the first display line.
So by pressing of
key you specify the second
display line. The consecutively pressed key will the be related to the second
display line instead of the first display line.
So by pressing of 
 the currency unit ATS will be assigned to the second line. If the currency unit
of the second line will be changed then the numerical value of the second line will
also be changed because the value of the first line will be converted to the new
currency unit of the second line.
the currency unit ATS will be assigned to the second line. If the currency unit
of the second line will be changed then the numerical value of the second line will
also be changed because the value of the first line will be converted to the new
currency unit of the second line.
Example:
How many Euro ( ), are 123.5 austrian Schilling (ATS).
), are 123.5 austrian Schilling (ATS).
 key.
key.
 .
.| Input | Display | |||||
| 123.5 | 123.5 8.98 | ATS |
Showing the 123.5 ATS of the last example in BEF:
| Input | Display | |||||
  | 23.5 362.05 | ATS BEF |
To start a new conversion, press the  key first to clear
the display and start a new input.
key first to clear
the display and start a new input.
| Input | Display | |||||
 |
0. 0.00 | ATS BEF | ||||
| 527.9 | 527.9 1547.60 | ATS BEF | ||||
  |
527.9 38.36 | ATS |
*  (exchange currencies) (exchange currencies) |
With this key the currencies of the first line and the second line can be exchanged. Only the currency units will be new assigned. The values will not be exchanged.
Example:
Conversions between various currencies.
| Input | Display | |||||
    |
0. 0.00 | DEM ATS | ||||
| 12.6 | 12.6 88.65 | DEM ATS | ||||
 | 12.6 0.92 | ATS DEM | ||||
 | 0. 0.00 | ATS DEM | ||||
| 100 | 100. 14.21 | ATS DEM |
*  (clear currency assignement) (clear currency assignement) |
If the  key is pressed, the currency assignement for
the first display line will be removed. So the number in the first display line has no unit.
Simultaneously the second display line will be hidden because a value without a unit
can not be converted to a number with a unit.
key is pressed, the currency assignement for
the first display line will be removed. So the number in the first display line has no unit.
Simultaneously the second display line will be hidden because a value without a unit
can not be converted to a number with a unit.
By pressing of 
 ,
the second line can be hidden without effecting the first line.
,
the second line can be hidden without effecting the first line.
Example:
| Input | Display | |||||
    |
0. 0.00 | DEM ATS | ||||
| 629.9 | 629.9 4431.68 | DEM ATS | ||||
  | 629.9 | DEM | ||||
  | 629.9 12991.98 | DEM BEF | ||||
 | 629.9 |
*  (specifies the number of decimal digits) (specifies the number of decimal digits) |
In combination with a number key, this key can be used to specify the number of
decimal digits (digits after the decimal point).
In combination with the  key, the number of decimal digits
for the second display line can be specified.
key, the number of decimal digits
for the second display line can be specified.
To remove the fixed number of digits after the decimal point and switch back to
floating point mode press 
 .
.
Note: The number of decimal digits can not be set during input of a number only after
a calculation or after pressing the  key.
key.
1. Specification of 3 decimal digits for the first line.
| Input | Display | |||||
 | 0. 0.00 | ATS DEM | ||||
 3 3 | 0.000 0.00 | ATS DEM | ||||
5  8 8  | 0.625 0.09 | ATS DEM |
2. Specification of 5 decimal digits for the second line.
| Input | Display | |||||
  5 5 | 0.625 0.08883 | ATS DEM |
3. Floating point display for the second line.
| Input | Display | |||||
   | 0.625 0.088834818282 | ATS DEM |
In CURRENCY mode the basic operations plus percent calculations can be performed as shown in SCIENTIFIC mode. However, currency units will be taken into account. So it is possible to perform calculations with mixed currency units.
Example:
Calculate 120 ATS + 20.5 DEM and show the result in DEM and Euro.
| Input | Display | |||||
    |
0. 0.00 | ATS | ||||
| 120 | 120. 8.72 | ATS | ||||
 | 120. 8.72 | ATS | ||||
| 20.5 | 20.5 1.49 | ATS | ||||
 | 20.5 10.48 | DEM | ||||
 | 37.55628511006 19.20 | DEM |
The result of calculations with currency units is displayed in the unit of the second operand, if one has been assigned. Otherwise, the unit of the first operand will be used for the result. Not all unit combinations are valid in calculations. The following table shows combinations of operations and their result units:
| Unit of operand 1 | Operation | Unit of operand 2 | Unit of result |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | + | B | B |
| A | none | (illegal op.) | |
| none | B | (illegal op.) | |
| none | none | none | |
| A | - | B | B |
| A | none | (illegal op.) | |
| none | B | (illegal op.) | |
| none | none | none | |
| A | × | B | (illegal op.) |
| A | none | A | |
| none | B | B | |
| none | none | none | |
| A | ÷ | B | none |
| A | none | A | |
| none | B | (illegal op.) | |
| none | none | none |
By trying to apply a illegal calculation, the calculator will be set into an error condition and
the symbol "E" will be displayed. The error condition can be cleared by pressing
the  key.
key.
On multiplications and divisions the calculator selects no unit for the second operand by default. But a unit can be assigned to the second operand explicitely.
Example:
| Input | Display | |||||
    |
0. 0.00 | ATS | ||||
| 1000 | 1000. 72.67 | ATS | ||||
 | 1000. 72.67 | ATS | ||||
| 2 | 2. | |||||
 | 500. 36.34 | ATS | ||||
| Input | Display | |||||
 |
0. 0.00 | ATS | ||||
| 1000 | 1000. 72.67 | ATS | ||||
 | 1000. 72.67 | ATS | ||||
| 20 | 20. | |||||
 | 20. 10.23 | DEM | ||||
 | 7.106785462526 |
After pressing an operator key ( ,
,  etc.)
or the keys
etc.)
or the keys  rsp.
rsp.  the currency unit
assigned to the value in the first line of the display will be shown in bold face.
This indicates, that the unit is dedicated to the value. Pressing a currency key in this situation
yields to a conversion of the value to the new currency and not the simple assignement of a
new currency to the value.
the currency unit
assigned to the value in the first line of the display will be shown in bold face.
This indicates, that the unit is dedicated to the value. Pressing a currency key in this situation
yields to a conversion of the value to the new currency and not the simple assignement of a
new currency to the value.
During the processing of complex expressions the calculator follows a set of predefined priorities which determine the sequence in which the operators have to be applied. In CURRENCY mode, the same rules for priority of operators and parenthesis are valid as described in SCIENTIFIC mode in section "Priority Levels of Operations".
The usage of the memories in CURRENCY mode is basically the same as in SCIENTIFIC mode.
With  a value will be stored in the
independently accessible memory and with
a value will be stored in the
independently accessible memory and with  a value can be added to the current memory contents.
Note that currency units are ignored when values are added to memory.
No currency conversion is performed.
The memory contents can be retrieved with the
a value can be added to the current memory contents.
Note that currency units are ignored when values are added to memory.
No currency conversion is performed.
The memory contents can be retrieved with the  key like usual.
key like usual.
In addition to the independently accessible memory, 10 memory slots are available
as in SCIENTIFIC mode which can be accessed with
 rsp.
rsp.  followed by a digit key.
followed by a digit key.
Normally the value in the first display line will be stored in the memory.
However, by using the  key the value of the second
display line can be stored.
Press one of the following key sequences:
key the value of the second
display line can be stored.
Press one of the following key sequences:

 ,
,

 for
independently accessible memory or
for
independently accessible memory or

 followed
by a digit key to store the value of the second line in one of the 10 memory slots.
followed
by a digit key to store the value of the second line in one of the 10 memory slots.
By default the twelve Euro related national currencies and the Euro are predefined in CURRENCY mode. Additionally, new currencys can be defined, currency definements can be changed or cleared.
The following table shows the predefined currencies with their currency symbols and conversion factors (exchange rates):
| Currency | Currency symbol | Exchange rate |
|---|---|---|
| Euro |  * * | 1.0 |
| Austria Schilling | ATS | 13.7603 |
| Belgium Franc | BEF | 40.3399 |
| Germany Mark | DEM | 1.95583 |
| Spain Peseta | ESP | 166.386 |
| Finland Markka | FIM | 5.94573 |
| France Franc | FRF | 6.55957 |
| Greece Drachma | GRD | 340.75 |
| Ireland Punt | IEP | 0.787564 |
| Italy Lira | ITL | 1936.27 |
| Luxembourg Franc | LUF | 40.3399 |
| Holland Guilder | NLG | 2.20371 |
| Portugal Escudos | PTE | 200.482 |
 ), that is, devices with a PalmOS version
less than 3.3, EUR will be displayed instead of the Euro symbol.
), that is, devices with a PalmOS version
less than 3.3, EUR will be displayed instead of the Euro symbol.
You can see in the table above that by default the base currency is Euro with has the factor (rate) of 1.0. The exchange ratings of all other currencies are related to the Euro. If a new currency should be defined, the exchange rate of that currency also has to be entered in relation to the Euro or another base currency has to be defined and all exchange rates have to be readapted to the new base currency.
The calculator uses the following formula for currency conversions:
Value2 = Value1 / Rate1 × Rate2 With the currency definition form a new currency can be defined, an existing
currency can be modified or deleted.
With the menu item "Define Currency Key..." in the "Options" menu
you switch into the currency definition mode.
With the currency definition form a new currency can be defined, an existing
currency can be modified or deleted.
With the menu item "Define Currency Key..." in the "Options" menu
you switch into the currency definition mode.
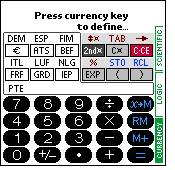
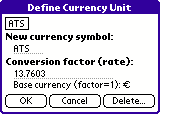 Here, the currency key to be defined
can be selected by pressing the key. All currency keys are located in the bordered region.
An undefined and therefore unlabeled currency key can also be selected to
define its currency.
Here, the currency key to be defined
can be selected by pressing the key. All currency keys are located in the bordered region.
An undefined and therefore unlabeled currency key can also be selected to
define its currency.
After selecting the currency key, the currency definition form appears. There the parameters of the currency can be changed and entered. With the key "Delete.." in the form, a currency definition can be erased.
To define a currency, a currency symbol consisting of up to
three charachters must be entered, which will be used as label for
the currency key. Also, the conversion factor (exchange rating)
related to the base currency has to be specified.
The base currency is displayed if one exists. Any currency
can be used as base currency by specifying conversion factor 1 for it.
Note: An alternative way to open the currency definition form for a currency key is to press the currency key for a period of at least 2 seconds and then releasing the key.
Example:
The currency US dollar should be added to the already defined currencies.
The currency key above the  key should
be used. The conversion factor should be 0.9174.
key should
be used. The conversion factor should be 0.9174.
 In the menu "Options" select the menu item "Define Currency Key..."
and then press the currency key you want to define.
In the menu "Options" select the menu item "Define Currency Key..."
and then press the currency key you want to define.
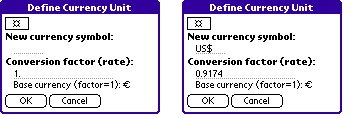 The currency definition form appears where the currency symbol US$ and
the conversion factor 0.9174 have to be entered. By pressing "OK" the
currency definition form will be closed and the currency is defined.
The currency definition form appears where the currency symbol US$ and
the conversion factor 0.9174 have to be entered. By pressing "OK" the
currency definition form will be closed and the currency is defined.
 The new currency is defined. It can be used:
The new currency is defined. It can be used:
| Input | Display | |||||
   |
0. 0.00 |  US$ | ||||
| 1 | 1. 0.92 |  US$ | ||||
  | 0. 0.00 | DEM US$ | ||||
| 64.55 | 64.55 30.28 | DEM US$ |
6. INPUTS |
Usually, the digits and operators will be entered by pressing the displayed keys. But all digits and some operators can also be entered using the Graffiti® region of the Palm device or pasted from the clipboard. Values can also be copied to the clipboard. Further it is possible to directly modify the contents of the memories in a special form.
 Starting with version 1.26 of the SC-103PC the memory manipulation form can
be opened via the menu item "Memory..." in the "Edit" menu.
In this form the contents of all memories can be seen simultaneously and they can
also be modified.
Starting with version 1.26 of the SC-103PC the memory manipulation form can
be opened via the menu item "Memory..." in the "Edit" menu.
In this form the contents of all memories can be seen simultaneously and they can
also be modified.
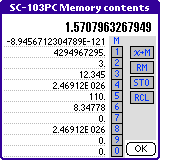 In the first line the actual display value is displayed.
In the following line the contents of the independently accessible memory (M) is
shown, followed by the 10 memories (1 to 9 and 0) which are assigned to the
number keys.
In the first line the actual display value is displayed.
In the following line the contents of the independently accessible memory (M) is
shown, followed by the 10 memories (1 to 9 and 0) which are assigned to the
number keys.
The actual display value can be stored in the independently accessible memory
by pressing the key  and can be restored using
the key
and can be restored using
the key  .
.
In addition to the independently accessible memory there are 10 memory slots are
available which can be modified with

 to
to 
 .
To read the contents of these memories you have to press the keys
.
To read the contents of these memories you have to press the keys 
 to
to 
 .
.
The memory contents can also be changed directly using Graffiti®.
By pressing "OK" the memory form will be closed and all entered values will be
written to the memories.
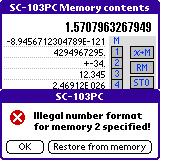 By pressing
By pressing  rsp.
rsp.  followed by a digit key or when selecting "OK", the entered values
will be written back to the memories. But first it will be checked if the
entered data is a valid value. If no valid value is entered an
error requester will be displayed. It can be closed by pressing "OK" to
correct the invalid input by hand. But if "Restore from memory" will be pressed,
the last memory contents will be restored and the input will be lost.
followed by a digit key or when selecting "OK", the entered values
will be written back to the memories. But first it will be checked if the
entered data is a valid value. If no valid value is entered an
error requester will be displayed. It can be closed by pressing "OK" to
correct the invalid input by hand. But if "Restore from memory" will be pressed,
the last memory contents will be restored and the input will be lost.
In the shown example a wrong input is done for memory location 2.
Following there is a table containing the keys which have been assigned a symbol which can be entered using Graffiti®
| SCIENTIFIC and CURRENCY Mode | LOGIC Mode | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Key: | Symbol: | Key: | Symbol: | |||
 to to  | "0" to "9" |  to to  | "0" to "9" | |||
 | ".", "," |  to to  | "a" to "f", "A" to "F" | |||
 | "_" |  | "_" | |||
 | " ", "C" |  | " " | |||
 | Backspace |  | Backspace | |||
 | "/" |  | "/" | |||
 | "*" |  | "*" | |||
 | "-" |  | "-" | |||
 | "+" |  | "+" | |||
 | "=", Enter |  | "=", Enter | |||
 | "(", "[", "{" |  | "(", "[", "{" | |||
 | ")", "]", "}" |  | ")", "]", "}" | |||
 | "%" |  | "&" | |||
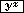 | "^" (only SCIENTIFIC) |  | "n", "N", "~" | |||
 | "!" (only SCIENTIFIC) |  | "o", "O", "|" | |||
 | "x", "X", "^" | |||||
 | "m", "M", "%" | |||||
 | "l", "L", "<"> | |||||
 | "r", "R", ">" | |||||
 With the menu items in the menu "Edit", the value currently shown on the display
can be cut or copied to the clipboard or a value in the clipboard
can be pasted to the SC-103PC.
With the menu items in the menu "Edit", the value currently shown on the display
can be cut or copied to the clipboard or a value in the clipboard
can be pasted to the SC-103PC.
7. ERRORS |
While in an error condition the display shows the symbol "E":

An error will be raised from a calculation or command which exceeds the
capacity of the program.
An error can be cleared by pressing the  key.
key.
 0
0  )
)
-1.7976931348624×10308 < x<= -2.23×10-308 for a negative x
2.23×10-308 <= x < 1.7976931348624×10308 for a positive x
The displayed value for x will be limited by the number of displayable positions.
Functions:
| Function | Range of x | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sin x cos x tan x |
DEG: |x| < 1.7976931348624×10308 RAD: |x| < 1.7976931348624×10308 GRAD: |x| < 1.7976931348624×10308 Further only for tan x: (n = integer) DEG: |x| 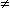 90(2n-1) 90(2n-1)RAD: |x| 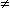 ( ( /2)(2n-1) /2)(2n-1)GRAD: |x| 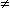 100(2n-1) 100(2n-1) |
|||||||||
| sin-1x cos-1x |
-1 <= x <= 1 | |||||||||
| tan-1x | |x| < 1.7976931348624×10308 | |||||||||
| sinh x cosh x | -710.47586007394 <= x <= 710.47586007394 | |||||||||
| tanh x | -1.7976931348623×10308 <= x <= 1.7976931348623×10308 | |||||||||
| sinh-1x | |x| < 1.3407807929943×10154 | |||||||||
| cosh-1x | 1 <= x < 1.3407807929943×10154 | |||||||||
| tanh-1x | |x| < 1 | |||||||||
| ln x log x |
2.23×10-308 <= x < 1.7976931348624×10308 | |||||||||
| ex | -1.7976931348624×10308 < x <= 709.78271289338 | |||||||||
| 10x | -1.3407807929943×10154 < x <= 308.25471555991 | |||||||||
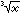 |
|x| < 1.7976931348624×10308 | |||||||||
| 1/x | |x| < 1.7976931348624×10308; x 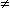 0 0 |
|||||||||
| x2 | |x| < 1.3407807929943×10154 | |||||||||
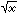 |
0 <= x < 1.7976931348624×10308 | |||||||||
| n! | 0 <= n <= 170 (n = integer) | |||||||||
DMS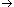 DEG DEGDEG  DMS DMS |
|x| < 1.7976931348624×10308 | |||||||||
| yx (yx=10x log y) |
|
|||||||||
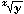 ( 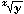 =101/x log y) =101/x log y) |
|
|||||||||
x, y 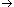 r, r,  |
|
|||||||||
r,  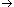 x, y x, y |
|